Factors Affecting Mixing Uniformity When Using an Intensive Mixer
During material mixing with an intensive mixer, mixing uniformity is one of the most critical indicators for evaluating mixing performance. Mixing uniformity not only affects the final product quality but is also directly related to production efficiency and cost control. Therefore, understanding and analyzing the factors that influence mixing uniformity is of great significance for optimizing mixing processes and improving product quality.
This article provides an in-depth discussion of the factors affecting mixing uniformity when using an intensive mixer, from multiple perspectives.
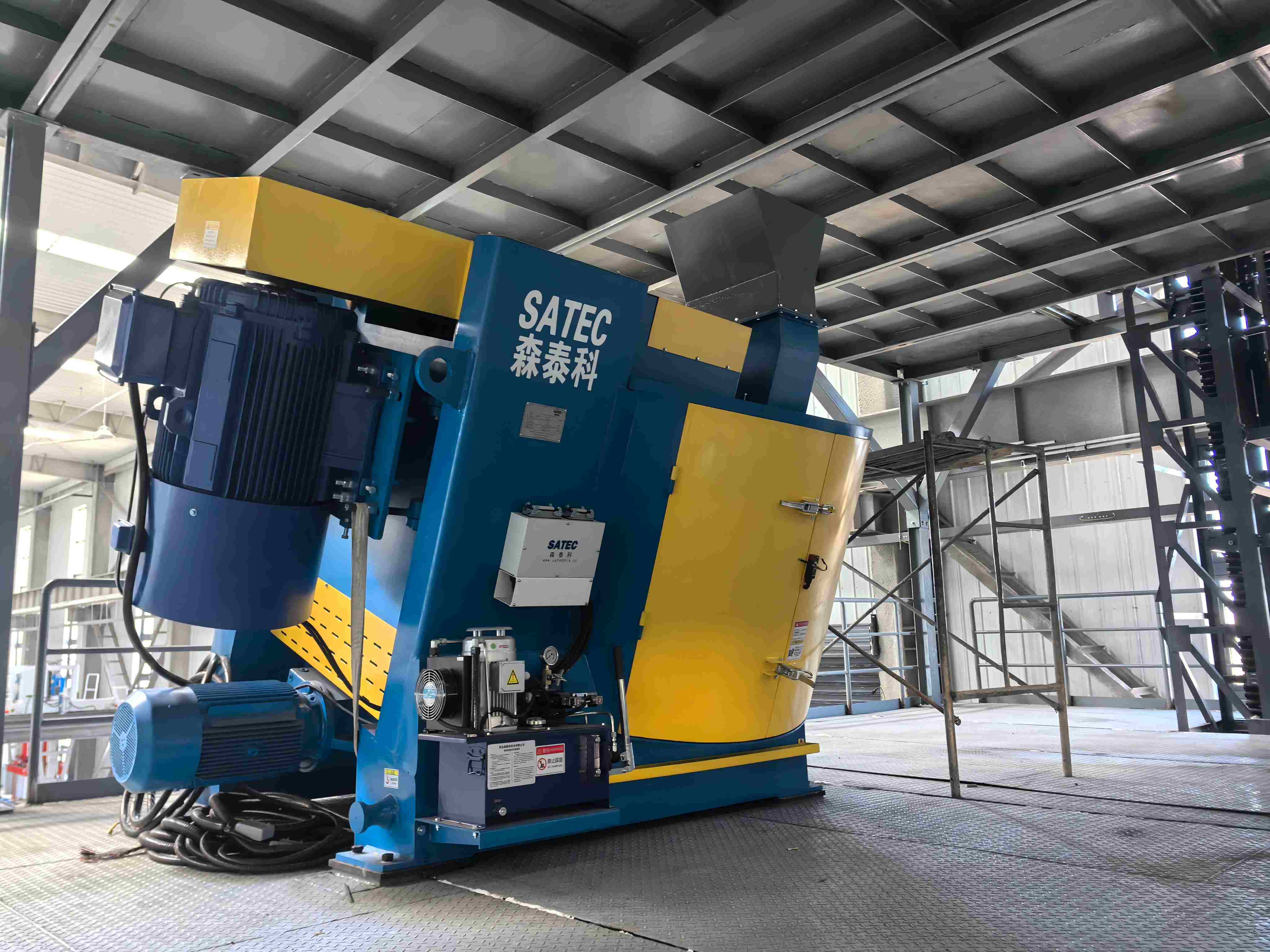

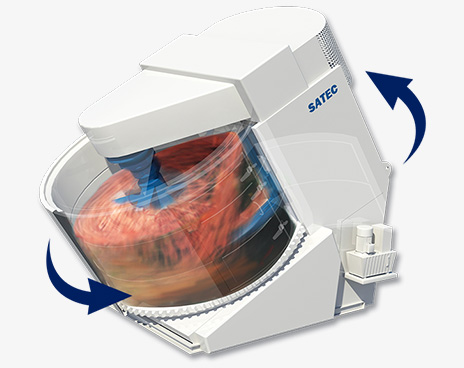
Intensive Mixer
I. Material Properties
Material properties are the primary factors affecting mixing uniformity, mainly including flowability, particle size, bulk density, and particle morphology.
1. Flowability
The flowability of materials directly affects their distribution and movement during the mixing process. Materials with poor flowability tend to adhere to each other, making it difficult for particles to interpenetrate, move, and convect, thereby reducing mixing uniformity. In contrast, materials with good flowability disperse and mix more easily within the mixer.
Therefore, pretreatment methods such as adding flow aids or adjusting material moisture content prior to mixing can effectively improve flowability and enhance mixing uniformity.
2. Particle Size
Differences in particle size have a significant impact on mixing uniformity. Coarse particles generally exhibit better compressibility but poorer formability, while fine particles have better formability but lower compressibility. Properly combining particles of different sizes can improve powder packing performance and compressibility, thereby enhancing the mixing effect.
However, when the particle size difference is too large, coarse particles tend to form a “skeleton” structure during mixing, hindering the diffusion and uniform distribution of fine particles and leading to poor mixing uniformity. Therefore, screening materials before mixing to reduce particle size differences is an effective way to improve uniformity.
3. Bulk Density
Materials with large differences in bulk density are prone to segregation during mixing. Light powders with low bulk density tend to float and remain on the upper layer, making it difficult for them to blend into heavier components, resulting in uneven mixing.
To mitigate this issue, pre-mixing materials before the main mixing process can help light and heavy powders achieve preliminary integration and reduce stratification.
4. Particle Morphology
Particle morphology also affects mixing uniformity. Irregularly shaped particles with rough surfaces are difficult to mix evenly, while smooth, spherical particles—although highly flowable—are prone to segregation during mixing.
Therefore, when selecting materials, particles with relatively regular shapes and smooth surfaces should be preferred to improve mixing uniformity.
II. Mixer Structure and Parameters
The structure of the mixer and its operating parameters also play a crucial role in determining mixing uniformity.
1. Mixer Type
Different types of mixers operate based on different mixing mechanisms. For example, horizontal ribbon mixers rely mainly on convective mixing, with relatively weak diffusion and shear effects. They offer fast mixing speeds but relatively lower uniformity.
Mixers dominated by diffusion mechanisms, such as drum mixers, operate more slowly and require longer mixing times but generally achieve higher mixing uniformity. Therefore, the appropriate mixer type should be selected based on material characteristics and mixing requirements.
2. Rotational Speed
The rotational speed of the mixer has a direct impact on mixing uniformity. Excessively high speeds may generate strong centrifugal forces, causing materials to accumulate along the edges of the mixing chamber and reducing uniformity. High speeds also increase equipment wear and energy consumption.
Thus, mixer speed should be set reasonably to balance mixing efficiency, uniformity, and equipment durability.
3. Filling Degree
The filling degree refers to the ratio of the material volume loaded into the mixer to the total mixer volume. When the filling degree is too low, there is insufficient material to generate effective mixing motion, resulting in poor uniformity. Conversely, when the filling degree is too high, overcrowding restricts material movement and also negatively affects uniformity.
Proper control of the filling degree is essential to achieve optimal mixing results.
4. Design of Mixing Pan and Rotor
The design of the mixing pan and rotor has a significant influence on mixing uniformity. The inclined mixing pan lifts materials upward during rotation; once materials reach a certain height, they fall back under gravity, creating coarse mixing. The rotor then applies high-intensity mixing action to achieve fine and uniform mixing.
Therefore, parameters such as the shape, size, and rotational speed of the mixing pan and rotor must be carefully designed and matched to ensure optimal mixing uniformity.
III. Operational Factors
Several operational factors during the mixing process also affect mixing uniformity.
1. Feeding Sequence
The feeding sequence has a considerable impact on mixing quality. Components with larger proportions should be fed into the mixer first, or largely loaded before adding minor or trace components. Small-quantity ingredients should be placed in areas where dispersion is easier.
This approach ensures sufficient contact between components and improves mixing uniformity.
2. Mixing Time
Mixing time directly affects mixing uniformity. If the mixing time is too short, materials cannot be fully mixed; if it is too long, excessive wear or agglomeration may occur, which can also reduce uniformity.
Therefore, mixing time should be optimized according to material properties and process requirements.
3. Monitoring and Adjustment During Mixing
During mixing, the operating status of the mixer should be continuously monitored, and parameters should be adjusted as needed. If segregation or material accumulation is observed, parameters such as rotational speed or mixing time should be adjusted promptly to improve uniformity.
IV. Other Influencing Factors
In addition to the factors mentioned above, several other aspects may also affect mixing uniformity.
1. Moisture Content
Material moisture content influences mixing behavior. Materials with excessive moisture tend to form agglomerates during mixing, reducing uniformity. Therefore, moisture levels should be controlled prior to mixing to avoid excessively high or low moisture content.
2. Residual Material in the Mixer
Residues left inside the mixer can negatively affect mixing uniformity. Residual materials may react with or contaminate newly added materials, leading to uneven mixing. Thus, thorough cleaning of the mixer before each batch is essential.
3. Environmental Factors
Environmental conditions such as temperature and humidity may also affect mixing uniformity. High temperatures may cause materials to soften or become sticky, while high humidity can lead to moisture absorption and caking—both of which impair mixing performance.
Therefore, environmental conditions should be controlled as much as possible during the mixing process to maintain stable mixing quality.
Conclusion
In conclusion, mixing uniformity in intensive mixers is influenced by a wide range of complex and interrelated factors. To achieve optimal mixing performance, it is essential to comprehensively consider material properties, mixer structure and parameters, operational practices, and environmental conditions, and to implement appropriate optimization measures.
Only through systematic analysis and process optimization can mixing uniformity meet quality requirements, thereby improving product quality and production efficiency.




 Environmental friendly
Environmental friendly Lithium battery
Lithium battery Chemical Industry
Chemical Industry Catalyst
Catalyst Ceramic
Ceramic Medical Food
Medical Food Metallurgy
Metallurgy Carbon
Carbon Fertilizer
Fertilizer Building materials
Building materials Foundry Sand
Foundry Sand Welding Flux
Welding Flux Glass
Glass Refractory
Refractory